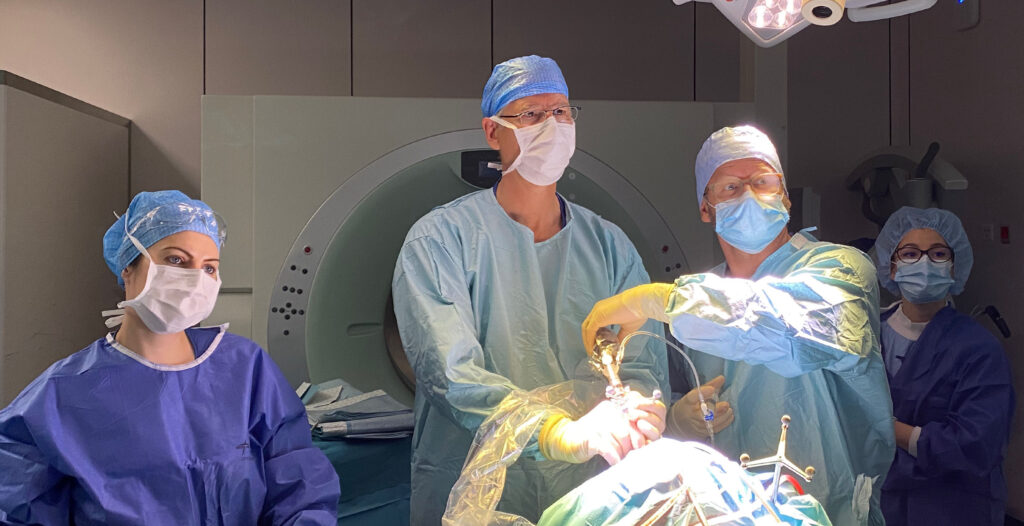
OPERATING THEATRES
EFFECTIVE, SAFE & GENTLE THANKS TO STATE-OF-THE-ART TECHNOLOGY
Our surgical department is the heart of our Centre. Up to 14 operating theatres are used every day. Of these, 3 rooms are specially equipped for neurosurgical procedures, one with intraoperative MRI, one with intraoperative CT and another “hybrid” operating room where we provide intraoperative angiography. This makes our centre the only one in Europe that can offer all the currently-available intraoperative imaging modalities.
The Centre is also equipped with the latest technology for microsurgery, endoscopy, documentation and image transmission. Elective operations of all levels of complexity are carried out each day apart from Sunday; emergencies of course are treated at any time of day or night.
INTRAOPERATIVE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
In 2009, the “BrainSUITE” by BrainLab was put into operation, and has been regularly upgraded since then. It is an operating theatre with a full-fledged computer tomograph (CT). This room is ideal for skull-base procedures, as CT scans are good at showing bony and solid skull-base tumours. Intraoperative CT is also very helpful in surgery to remove a tumour of the pituitary gland or a tumour of the meninges (meningioma). Before the cranial opening is completely closed, new images can be taken and the surgical result can be checked. The patient therefore leaves the operating room only if everything is in order, in other words if the tumour has been removed according to plan, and complications have been ruled out.
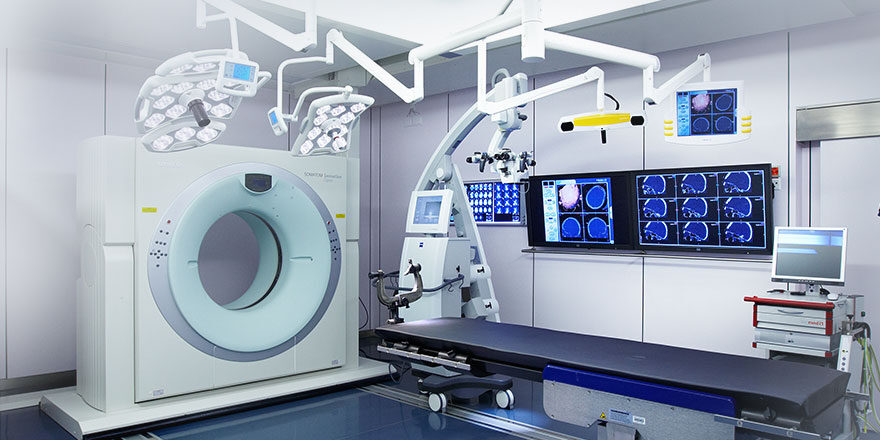
INTRAOPERATIVE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
In 2012, another operating room was converted for the operation of an intraoperative magnetic resonance tomograph. The PoleStar N30 is an innovative mobile magnetic resonance tomograph which can be used directly at the operating table and allows the use of regular instruments and equipment. This gives it a very great advantage over other systems. The use of intraoperative nuclear spin tomography is particularly helpful in brain tumour operations, since it allows the soft tissues of the brain to be imaged particularly well and residual tumour parts to be reliably identified thanks to neuronavigation. Preparing an intraoperative MRI requires a great deal of technical effort and time. However, the effort is worthwhile, since with many brain tumours, a complete tumour resection demonstrably improves the progression-free survival time.
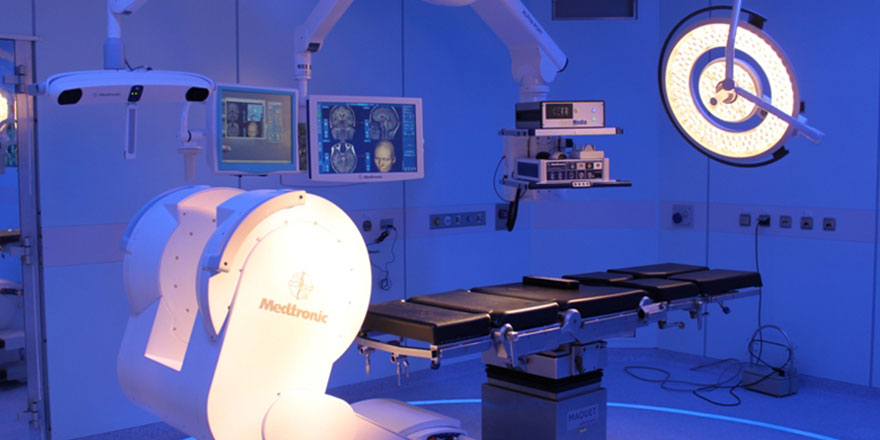
INTRAOPERATIVE ANGIOGRAPHY (HYBRID SURGERY)
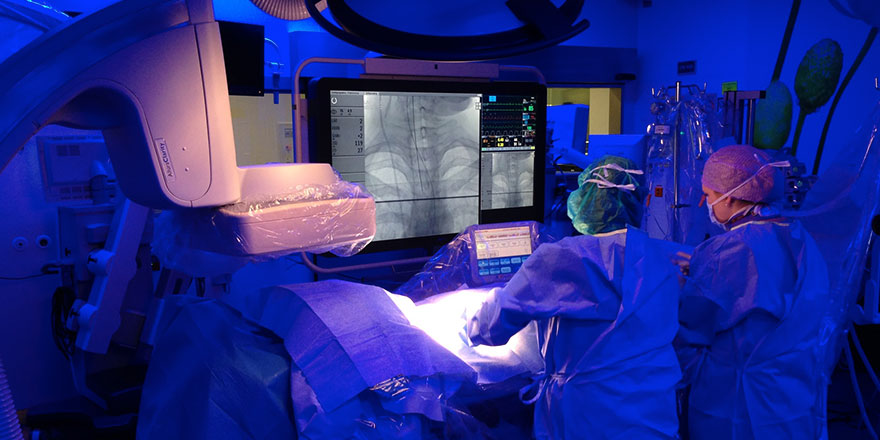
INTRAOPERATIVE FUNCTIONAL MONITORING
All neurosurgical interventions in functionally important areas of the brain and spinal cord are carried out while monitoring the respective function. In most cases this can be done under anaesthetic. This is not possible only in the case of speech and other higher cortical functions such as arithmetic, writing and reading. For these functions, intraoperative functional monitoring can only be carried out during awake surgery. [LINK TO AWAKE SURGERY]
Functional monitoring, or electrophysiological monitoring, is carried out using various methods. It is used in particular to detect spontaneous and stimulated activity of nerve cells (EEG, EP) as well as the spontaneous and stimulated activity of muscles (EMG).
Intraoperative EEG is particularly helpful in patients affected by epileptic seizures. Intraoperative electrocorticography (ECoG) uses electrodes placed directly on the surface of the brain to identify the areas that cause epilepsy and then remove them.
With the help of EPs, the sensation (SEP) and movement (MEP) of the arms and legs as well as vision (VEP) and hearing (AEP) can be monitored. Both the strength of the response and the speed of propagation play an important role in the assessment.
EMG derivations provide important information about the function of relevant cranial nerve functions such as the facial nerve, the ocular muscle nerves and the swallowing nerve through the occurrence of spontaneous activity or the reaction to targeted stimulation. This technique can also be used to specifically identify the nuclei of origin of individual nerves in the brain stem and to protect them accordingly.
Functional monitoring improves the retention of essential neurological functions and thus the safety of neurosurgical operations. In addition, this method has enabled us to safely and effectively tackle a disease that has hitherto been regarded as inoperable.
COMPUTER-AIDED SURGERY NEURONAVIGATION
Neuronavigation is a method of intraoperative orientation based on imaging data. By comparing a 3D computer model of the patient’s head from the corresponding high-resolution CT or MRI data against the patient’s head in the operating room, it is possible to match the image data to the patient’s head with millimetric accuracy. Thus, the exact position and extent of a tumour can be projected onto the surface of the patient’s head or even after opening of the skull, onto the exposed areas of the brain. This procedure helps the surgeon gauge the planned access and the direction of the preparation and thus also to reach deep-seated lesions in the most gentle way. The neuronavigation enables a corresponding orientation even in the case of greatly altered or confusing anatomy.
Neuronavigation is now used in virtually all neurosurgical operations on the skull, and is now an integral part of modern minimally invasive neurosurgery.
Augmented Reality (AR)
It is already possible today to integrate into the navigation system additional information from preoperative diagnostics and operation planning, such as nerve tract systems, functional centres and tumour borders. It is also possible to integrate intraoperatively acquired, updated imaging data from ultrasound devices, angiography systems and computer and nuclear magnetic resonance tomographs, and thus to image the current state of the operation in each case. Using high-performance computer systems, this information can be fed into video images of surgical microscopes and endoscopes in real time. This technique is also called augmented reality. Technically extremely complex, this method is currently reserved for particularly complex operations, and cannot yet be regarded as a routine method.
FLUORESCENCE GUIDED SURGERY
Fluorescence-guided surgery is used in the removal of rapidly-growing brain tumours and in operations on brain vessels. Depending on the fluorescent substance used in the operation, a light of a certain wavelength is emitted by the surgical microscope. This allows the identification of tumour cells which, in contrast to healthy cells, are not capable of degrading the fluorescent substance and show up as bright red. The blood flow can be represented by admixing a short-acting green fluorescent substance, even in very small vessels.
The fluorescence-guided resection of tumours has become an established procedure for fast-growing gliomas and certain metastases. Numerous publications show that the use of this technique can improve the prognosis of the disease. Where there is the suspicion of this type of tumour, the patient will be administered 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA: Gliolan®), which must be dissolved in water and drunk 3-5 hours before the operation. The metabolic product protoporphyrin accumulates selectively in the tumour cells, which cannot further degrade this molecule and fluoresce into a salmon-red colour.
The combination of fluorescence-assisted resection technology with intraoperative MR imaging and the use of endoscopes has the potential to further improve radicality while maximising brain function.
The use of the fluorescent substance indocyanine green (ICG) makes it possible to achieve high-resolution intraoperative vascular imaging without X-rays. The ICG is injected into a vein. With the help of infrared light from a special light source on the surgical microscope or endoscope, the blood flow of the vessels lying on the surface is visible in real time. At our centre, this procedure is used for every aneurysm and AVM operation in order to ensure an optimal surgical result, and at the same time maximum safety for the patient. The combination of ICG fluorescence technology and conventional angiography in the hybrid operating theatre, combined with the use of endoscopes, promises further optimisation of the surgical possibilities for vascular neurosurgery.
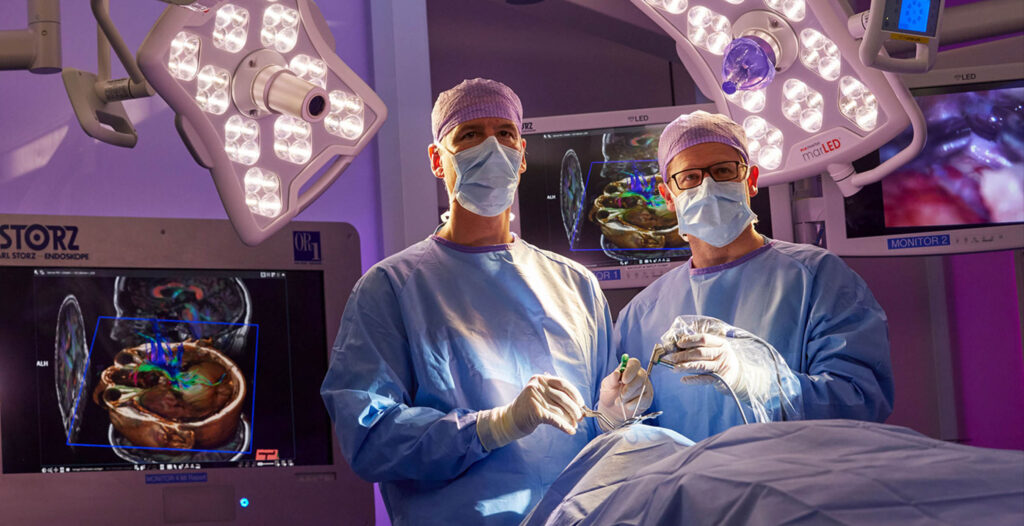
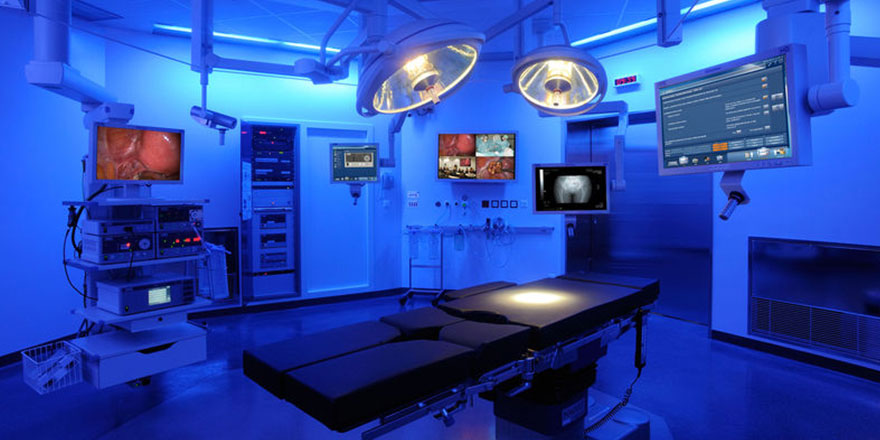
NETWORKED OP (OR1)
The OR1 room was built with the assistance of the company Karl Storz: here neuroendoscopy comes to the fore. Microscope-based and endoscopic surgical techniques are optimally combined with electromagnetic and optical navigation. All the devices in the room can be controlled by a central unit and each step of the operational process can be documented. The backlighting can be chosen according to the preferences of the surgeon, creating a calming atmosphere for this highly concentrated work.
Another key benefit is the real-time transmission of operations for surgical courses and online webinars.
Für Rückfragen
+41 44 387 28 29
Behandlungsanfrage
Glückliche Patienten


Fragen und Antworten
zur endoskopischen Neurochirurgie